|
Richard Rado
Richard Rado FRS (28 April 1906 – 23 December 1989) was a German-born British mathematician whose research concerned combinatorics and graph theory. He was Jewish and left Germany to escape Nazi persecution. He earned two PhDs: in 1933 from the University of Berlin, and in 1935 from the University of Cambridge. He was interviewed in Berlin by Lord Cherwell for a scholarship given by the chemist Sir Robert Mond which provided financial support to study at Cambridge. After he was awarded the scholarship, Rado and his wife left for the UK in 1933. He was appointed Professor of Mathematics at the University of Reading in 1954 and remained there until he retired in 1971. Contributions Rado made contributions in combinatorics and graph theory including 18 papers with Paul Erdős. In graph theory, the Rado graph, a countably infinite graph containing all countably infinite graphs as induced subgraphs, is named after Rado. He rediscovered it in 1964 after previous works on the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading, Berkshire
Reading ( ) is a town and borough in Berkshire, England, and the county town of Berkshire. It is the United Kingdom's largest town, with a combined population of 355,596. Most of Reading built-up area, its built-up area lies within the Borough of Reading, although some outer suburbs are parts of neighbouring local authority areas. It is located in the Thames Valley at the confluence of the rivers River Thames, Thames and River Kennet, Kennet. Reading is a major commercial centre, especially for information technology and insurance. It is also a regional retail centre, serving a large area of the Thames Valley with its shopping centres, including The Oracle, Reading, the Oracle, the Broad Street Mall, and the pedestrianised area around Broad Street. It is home to the University of Reading. Every year it hosts the Reading and Leeds Festivals, Reading Festival, one of England's biggest music festivals. Reading has a professional association football team, Reading F.C., and partici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
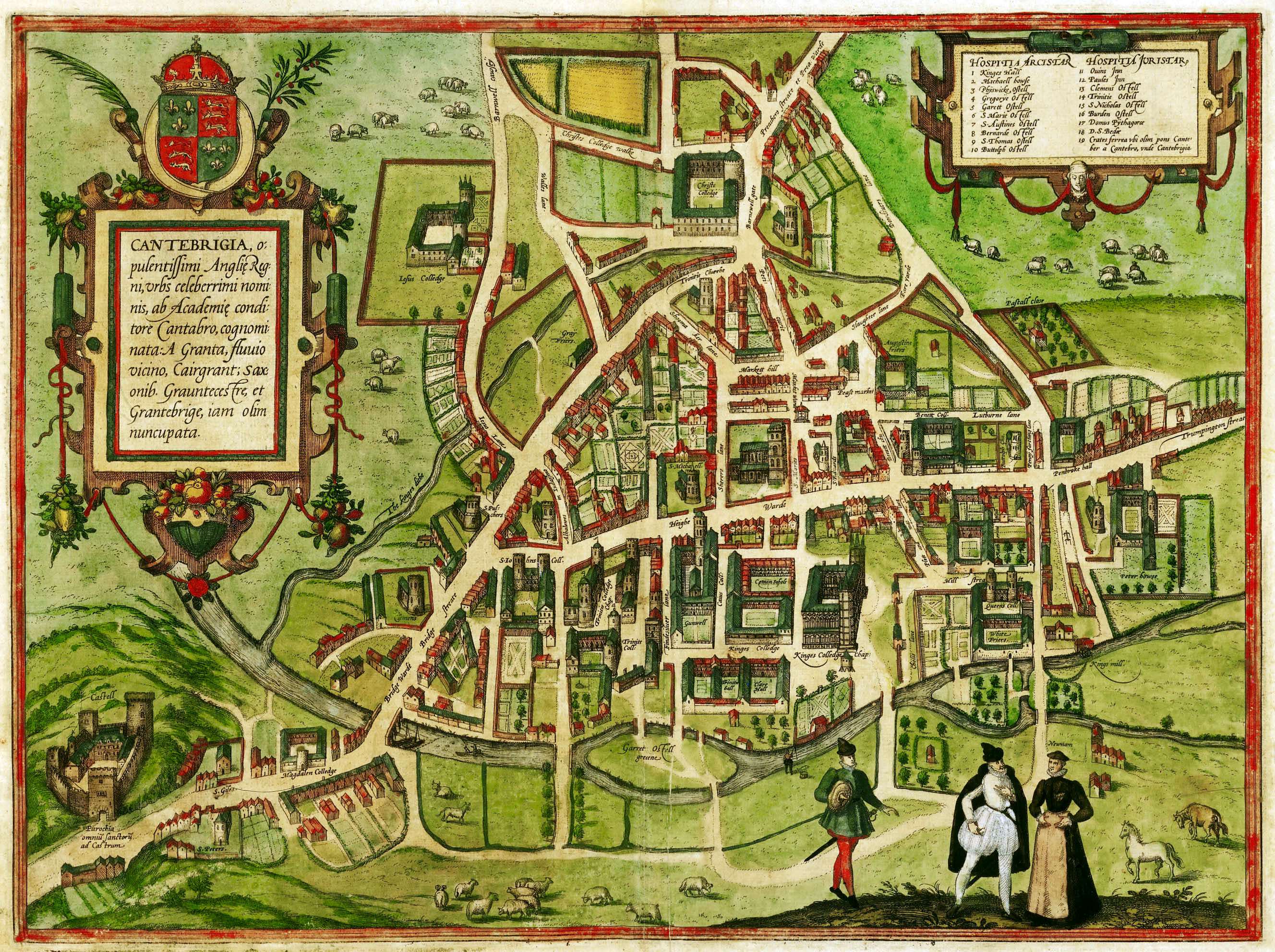
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transversal (combinatorics)
In mathematics, particularly in combinatorics, given a family of sets, here called a collection ''C'', a transversal (also called a cross-section) is a set containing exactly one element from each member of the collection. When the sets of the collection are mutually disjoint, each element of the transversal corresponds to exactly one member of ''C'' (the set it is a member of). If the original sets are not disjoint, there are two possibilities for the definition of a transversal: * One variation is that there is a bijection ''f'' from the transversal to ''C'' such that ''x'' is an element of ''f''(''x'') for each ''x'' in the transversal. In this case, the transversal is also called a system of distinct representatives (SDR). * The other, less commonly used, does not require a one-to-one relation between the elements of the transversal and the sets of ''C''. In this situation, the members of the system of representatives are not necessarily distinct. In computer science, comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matroid
In combinatorics, a matroid is a structure that abstracts and generalizes the notion of linear independence in vector spaces. There are many equivalent ways to define a matroid Axiomatic system, axiomatically, the most significant being in terms of: independent sets; bases or circuits; rank functions; closure operators; and closed sets or ''flats''. In the language of partially ordered sets, a finite simple matroid is equivalent to a geometric lattice. Matroid theory borrows extensively from the terms used in both linear algebra and graph theory, largely because it is the abstraction of various notions of central importance in these fields. Matroids have found applications in geometry, topology, combinatorial optimization, network theory, and coding theory. Definition There are many Cryptomorphism, equivalent ways to define a (finite) matroid. Independent sets In terms of independence, a finite matroid M is a pair (E, \mathcal), where E is a finite set (called the ''gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chao Ko
Ke Zhao or Chao Ko (, April 12, 1910 – November 8, 2002) was a Chinese mathematician born in Wenling, Taizhou, Zhejiang. Biography Ke graduated from Tsinghua University in 1933 and obtained his doctorate from the University of Manchester under Louis Mordell in 1937. His main fields of study were algebra, number theory and combinatorics. Some of his major contributions included his work on quadratic forms, the Erdős–Ko–Rado theorem and his theorem on Catalan's conjecture. In 1955, he was one of the founding members of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He was later a professor at Sichuan University Sichuan University
Sichuan University (SCU) is a public university in Chengdu, Sichuan, C ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypergraph
In mathematics, a hypergraph is a generalization of a Graph (discrete mathematics), graph in which an graph theory, edge can join any number of vertex (graph theory), vertices. In contrast, in an ordinary graph, an edge connects exactly two vertices. Formally, a directed hypergraph is a pair (X,E), where X is a set of elements called ''nodes'', ''vertices'', ''points'', or ''elements'' and E is a set of pairs of subsets of X. Each of these pairs (D,C)\in E is called an ''edge'' or ''hyperedge''; the vertex subset D is known as its ''tail'' or ''domain'', and C as its ''head'' or ''codomain''. The order of a hypergraph (X,E) is the number of vertices in X. The size of the hypergraph is the number of edges in E. The order of an edge e=(D,C) in a directed hypergraph is , e, = (, D, ,, C, ): that is, the number of vertices in its tail followed by the number of vertices in its head. The definition above generalizes from a directed graph to a directed hypergraph by defining the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Number
In set theory, an ordinal number, or ordinal, is a generalization of ordinal numerals (first, second, th, etc.) aimed to extend enumeration to infinite sets. A finite set can be enumerated by successively labeling each element with the least natural number that has not been previously used. To extend this process to various infinite sets, ordinal numbers are defined more generally using linearly ordered greek letter variables that include the natural numbers and have the property that every set of ordinals has a least or "smallest" element (this is needed for giving a meaning to "the least unused element"). This more general definition allows us to define an ordinal number \omega (omega) to be the least element that is greater than every natural number, along with ordinal numbers , , etc., which are even greater than . A linear order such that every non-empty subset has a least element is called a well-order. The axiom of choice implies that every set can be well-orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rado's Theorem (Ramsey Theory)
Rado's theorem is a theorem from the branch of mathematics known as Ramsey theory. It is named for the German mathematician Richard Rado. It was proved in his thesis, ''Studien zur Kombinatorik''. Statement Let A \mathbf = \mathbf be a system of linear equations, where A is a matrix with integer entries. This system is said to be r''-regular'' if, for every r-coloring of the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, ..., the system has a monochromatic solution. A system is ''regular'' if it is ''r-regular'' for all ''r'' ≥ 1. Rado's theorem states that a system A \mathbf = \mathbf is regular if and only if the matrix ''A'' satisfies the ''columns condition''. Let ''ci'' denote the ''i''-th column of ''A''. The matrix ''A'' satisfies the columns condition provided that there exists a partition ''C''1, ''C''2, ..., ''C''''n'' of the column indices such that if s_i = \Sigma_c_j, then # ''s''1 = 0 # for all ''i'' ≥ 2, ''si'' can be written as a ration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramsey's Theorem
In combinatorics, Ramsey's theorem, in one of its graph-theoretic forms, states that one will find monochromatic cliques in any edge labelling (with colours) of a sufficiently large complete graph. To demonstrate the theorem for two colours (say, blue and red), let and be any two positive integers. Ramsey's theorem states that there exists a least positive integer for which every blue-red edge colouring of the complete graph on vertices contains a blue clique on vertices or a red clique on vertices. (Here signifies an integer that depends on both and .) Ramsey's theorem is a foundational result in combinatorics. The first version of this result was proved by Frank Ramsey. This initiated the combinatorial theory now called Ramsey theory, that seeks regularity amid disorder: general conditions for the existence of substructures with regular properties. In this application it is a question of the existence of ''monochromatic subsets'', that is, subsets of connected edges o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatorial Set Theory
In mathematics, infinitary combinatorics, or combinatorial set theory, is an extension of ideas in combinatorics to infinite sets. Some of the things studied include continuous graphs and trees, extensions of Ramsey's theorem, and Martin's axiom. Recent developments concern combinatorics of the continuum and combinatorics on successors of singular cardinals. Ramsey theory for infinite sets Write \kappa, \lambda for ordinals, m for a cardinal number (finite or infinite) and n for a natural number. introduced the notation as a shorthand way of saying that every partition of the set kappan of n-element subsets of \kappa into m pieces has a homogeneous set of order type \lambda. A homogeneous set is in this case a subset of \kappa such that every n-element subset is in the same element of the partition. When m is 2 it is often omitted. Such statements are known as partition relations. Assuming the axiom of choice, there are no ordinals \kappa with \kappa\rightarrow(\omega)^, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfréd Rényi
Alfréd Rényi (20 March 1921 – 1 February 1970) was a Hungarian mathematician known for his work in probability theory, though he also made contributions in combinatorics, graph theory, and number theory. Life Rényi was born in Budapest to Artúr Rényi and Borbála Alexander; his father was a mechanical engineer, while his mother was the daughter of philosopher and literary critic Bernhard Alexander; his uncle was Franz Alexander, a Hungarian-American psychoanalyst and physician. He was prevented from enrolling in university in 1939 due to the anti-Jewish laws then in force, but enrolled at the University of Budapest in 1940 and finished his studies in 1944. At this point, he was drafted to forced labour service, from which he managed to escape during transportation of his company. He was in hiding with false documents for six months. Biographers tell an incredible story about Rényi: after half of a year in hiding, he managed to get hold of a soldier's uniform and march ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Ackermann
Wilhelm Friedrich Ackermann (; ; 29 March 1896 – 24 December 1962) was a German mathematician and logician best known for his work in mathematical logic and the Ackermann function, an important example in the theory of computation. Biography Ackermann was born in Herscheid, Germany, and was awarded a Ph.D. by the University of Göttingen in 1925 for his thesis ''Begründung des "tertium non datur" mittels der Hilbertschen Theorie der Widerspruchsfreiheit'', which was a consistency proof of arithmetic apparently without Peano induction (although it did use e.g. induction over the length of proofs). This was one of two major works in proof theory in the 1920s and the only one following Hilbert's school of thought. From 1929 until 1948, he taught at the Arnoldinum Gymnasium in Burgsteinfurt, and then at Lüdenscheid until 1961. He was also a corresponding member of the Akademie der Wissenschaften (''Academy of Sciences'') in Göttingen, and was an honorary professor at the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |